Limits of Bitcoin and Lightning Network: brief introduction
Scaling Bitcoin by making it super-performant? Thanks to Lightning Network, it is possible.
We are about to delve into the discovery of an often little considered but highly valuable Layer 2 solution.
We all know bitcoin, the undisputed queen of the crypto universe. From being an experiment and “toy” for geeks, this cryptocurrency has over time gathered more and more acceptance, becoming a store of value in constant adoption.
However, the Bitcoin blockchain has several limitations related mainly to the issue of scalability:
- The creation of a block takes 10 minutes. It also contains a limited number of movements.
- Related to the previous point, Bitcoin has a maximum threshold of 7 transactions per second. Therefore, queues are easily created.
- As slowdowns form, a single transaction can take a very long time to complete in periods of high congestion.
- Finally, given that “the more you pay in fees the better off you are,” the cost of a transaction can be significantly high. In addition, this mechanism contributes to even longer queues.
Summed up in a nutshell: for everyday payments, especially those involving small amounts, Bitcoin is not efficient.
As is well known, mass adoption of cryptocurrencies also comes through everyday use. Actions such as shopping for groceries, buying a book or selling one’s products should also be able to be accomplished by these means.
Given these assumptions, Bitcoin does not stand out as the best solution in this regard.
A fantastic feature of our industry is the ability to find a way to eliminate problems. In fact, blockchain technology lends itself to integrations, modifications and applications that enhance what already exists. So here comes Lightning Network, the ingenious remedy to Bitcoin’s limitations.
After an initial section aimed at better framing this layer 2, we will devote a section on how to interact with it. Obviously there will be more to explore independently depending on the medium employed, however, we will lay some very useful groundwork.
So let us see what Lightning Network is.
Index
What is the Lightning network?
The official definition of Lightning Network tells us that “Lightning is a decentralized network using smart contract functionality in the blockchain to enable instant payments across a network of participants.” Let’s try to clarify this.
Lightning is a decentralized network, layer 2 of Bitcoin. By using smart contract functionality in the blockchain, instant payments can be processed.
Let’s start with a fundamental concept: layer 2. Lightning is a network built on top of Bitcoin, its layer 1; it could not exist without the parent blockchain and would serve no purpose anyway.
Layer 2s are solutions designed to enhance the underlying network in some way. For example, Ethereum has several such networks (such as Arbitrum and Polygon) that overcome its limitations and expand the proposition. Lightning has precisely this role: to give Bitcoin something more.
For the more curious, our article on layer 0, layer 1 and layer 2 is the perfect place to learn more about them.
In the previous paragraph, we listed the limitations of Bitcoin, coming to the conclusion that it is not exactly the best technology available for the world of micropayments.
Who would want to wait tens of minutes, if not hours, before being able to complete a payment?
What individual would be willing to spend high fees, perhaps higher than the good purchased?
In general, how can one expect the crypto revolution to come to every business if the underlying technology supports only 7 transactions per second? VISA, the famous electronic payment circuit, processes thousands.
Lightning Network is the technical solution that makes Bitcoin a blockchain absolutely capable of coping with high traffic loads, far exceeding that of the just-mentioned VISA.
This layer 2 has solid and important strengths:
- Speed: it is a very fast network, capable of completing transactions instantly;
- Cost-effectiveness: gas fees are negligible, almost zero;
- Number of transactions: in addition to being fast, this Layer 2 could potentially support hundreds of thousands and even millions of movements per second.
Finally, let us add that it is constantly growing (see graphs just below).
At this point there should be some curiosity about Lightning Network.
Questions such as “How is this possible?” and “What solution have they adopted to achieve such milestones?” will probably go through the mind.
So let’s waste no more time and unravel the mystery!
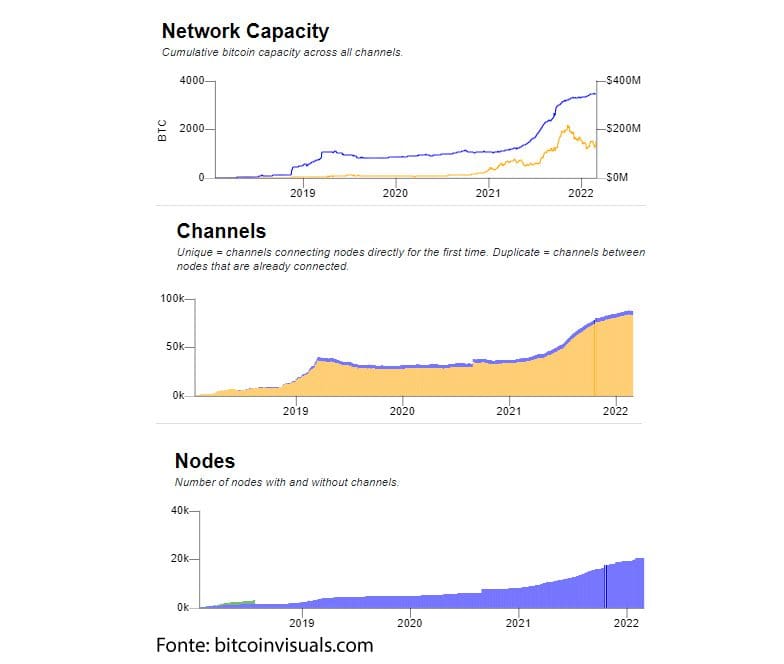
How does Lightning Network work?
To understand how Lightning Network works, we need to resort to a few examples and introduce Payment Channels.
First, let’s imagine that we go to a coffee shop to get a coffee, deciding to pay for it in bitcoin.
Given the issues we have already discussed, we will spend significantly more than the amount of the drink in gas fees.
I mean, it’s not the best to drop almost €5 for a coffee, is it? At other times it could easily have cost as much as 20, 30 0 50: if there is a lot of demand, gas fees soar.
Let’s take it one step further: we have coffee at the café every day.
Here, here the problem would be further amplified: for once we could even spend 5€ but every day just no!
However, we find a solution by asking the barista to keep an account open. At the end of the month we will pay for all the coffees consumed, compressing them into a single transaction and drastically lowering the cost of gas fees.
Of course, there are still limits: it is not possible to open an account at every business attended. Even if it were, at the end of the month we would have to travel halfway across town just to pay off our debts. Barriers would still remain: for example, how to make a single purchase?
Therefore, we need to find a method that really contains gas fees for each movement, usable anywhere and applicable to any type of buying and selling.
Payment Channels: the starting point to solving the problem
Payment Channels partially meet this profile. These are precisely payment channels that trace the bar account model.
Two parties open a channel on the blockchain through a multisig transaction, paying a certain initial capital.
At this point, they can send as many transactions to each other as they want without paying any fees. Absurdly, they could spend the day bouncing each other an amount; there would be no problem. This is because the channel operates off-chain, not interacting in any way with the blockchain until it is closed.
When you get to the point where you want to end the transactions, the channel is terminated, the transaction sent to layer 1 and the sums updated.
By doing so, the number of transactions is lowered and, consequently, the associated costs. Not only that, the blockchain is not burdened as most of the work is done off-chain.
As we said, this system takes inspiration from the classic bar tab: it accomplishes transactions but does not record them until the channel is closed. Exactly what the bartender does: he marks the consumptions on a sheet of paper and periodically comes right to claim what is due.
Payment channels have limitations, however:
- They support only two parties: me and the bartender, you and the mechanic, and Satoshi and his friend Vitalik. This is a huge stumbling block: how many channels would have to be opened if we wanted to pay for all our purchases with bitcoin?
- Continuous opening and closing: payment channels have limited uptime and still require continuous opening and closing. Therefore, they are not practical as an extended form of payment: the goal is to reduce time and cost, and opening channels go-go would achieve neither.
So what is the remedy?
Lightning Network: instant bitcoin payments at negligible cost
Finally, we come to the subject of this in-depth study.
The Lightning network takes advantage of the payment channels mechanism but removes its limitations. The result is a reliable and sustainable system designed for bitcoin micropayments.
Lightning is a network of nodes that share liquidity and leverage smart contracts to work in synergy.
There is no longer a need to open a channel with each person; we will rely on others to get our BTC to its destination.
We will in fact be leveraging existing channels, the only key is that the recipient has at least one.
For example, if Alice were to send bitcoins to Dan, they could go through Bob’s node, bounce to Carol’s node, and finally reach their destination.
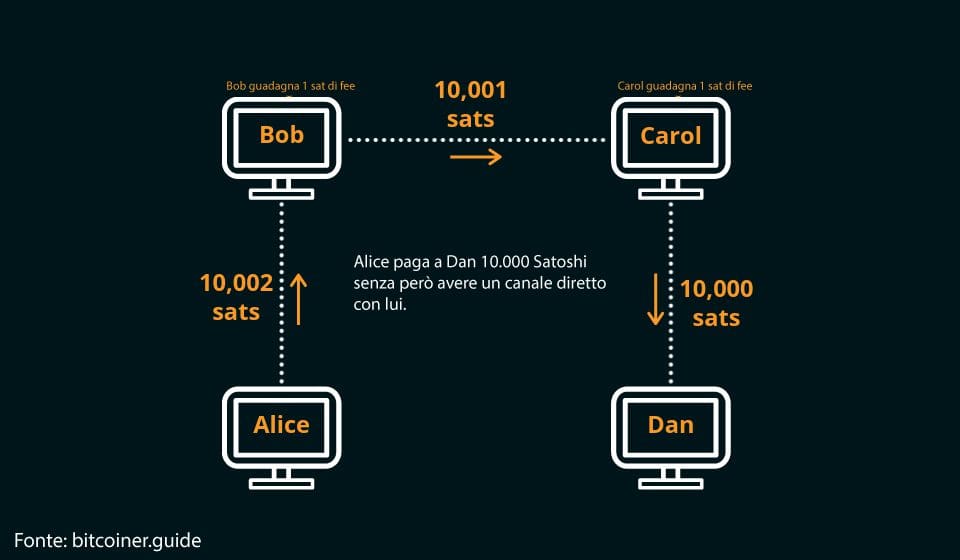
The advantages of this system are numerous:
- One does not have to open a channel with each counterparty. Doing so cuts down on time and costs: starting a channel would in fact require a transaction on the blockchain. Same goes for its subsequent closure.
- Movements are very fast, virtually instantaneous. This is critical for everyday payments.
- Transactions are priced negligibly. My €1 coffee will come to cost a few thousandths more, not €5!
- By operating off-chain, privacy is assured.
- The blockchain provides security. If one party were to attempt to make tampering, Layer 1 would be able to detect the problem.
In these situations, the blockchain becomes a kind of “judge” and assigns punishment to the offender, i.e., the forced withdrawal of a share or even all of its funds, turned over to the offending party.
Obviously, the system needs two basic elements for proper functioning: paid-up capital and a large catchment area.
On capital, this is important because it is through it that transactions are reduced to the bone.
Going back to the example brought up just now, if Bob and Carol had not deposited bitcoins, sending funds from Alice to Dan would not be possible through this system. A dedicated channel would have to be set up, with all the costs and timing that entails.
The catchment area is equally pivotal: the larger the network, the greater its ubiquity. Also, related to the previous point, there is superior availability of funds.
Maintaining a channel on Lightning Network is incentivized by commissions. In fact, the reduced gas fees end up with those who make stability and operation of the system possible. These are small amounts in recognition of the service provided.
Weaknesses of Lightning Network
As good a service as it is, Lightning is not without its weaknesses. Specifically, the main ones are two:
- Sender and receiver of a transaction must both be online. This is because a double check must be performed between the parties during the transaction so that security and fairness can be guaranteed.
- Issues due to the centralization of capital. The network needs funds in order to function; therefore, large players with substantial resources could take over, increasing its centralization.
However, as far as we have seen so far, Lightning is an excellent remedy to Bitcoin’s known limitations. Through it, the famous cryptocurrency becomes truly expendable in everyday life. Thankfully, use cases and intrinsic value grow.
First we piqued curiosity. Later expanded knowledge. But now we need to take the next step: finding out how to interact with this excellent layer 2.
"Fast, quick, secure: Lightning Network brings bitcoin to the world of micropayments effortlessly!"
How to interact with Lightning Network
Entering the world of Lightning Network is not complex: you just need to know and download the correct tools.
There are several options available, but here we will explore only the most popular and easy to configure ones.
As a first choice we can opt for Blue Wallet. This is a mobile wallet that offers several services; among them is, of course, full support for the Lightning network.
Simply go to bluewallet.io and click on the desired version button between Android and IOS.
Once downloaded, a quick setup will be required but fear not: the procedure is simple and guided.
In any case, here are some step-by-step tips on how to get going:
- Install the application on the mobile device of our interest.
- After opening it, click on the “Add Now” button in the window labeled “Add a wallet.” You can name the wallet we are going to create.
- Select Lightning and save the retrieval QR Code that will be shown on the screen. Procedure completed, super easy, right?
Blue Wallet can also serve the function of a classic bitcoin wallet or a safe, the latter suitable for keeping large sums safe.
No need to configure any nodes or channels: you are already automatically up and running on LDNhub; one less thought to worry about.
To deposit funds, simply click on the large orange background “Wallet” button and follow the instructions to proceed.
Capital exchange is also simple and based on QR Code scanning, which is very convenient and quick to do.
You just need to experiment a bit and get familiar with it but nothing complex; Blue Wallet is designed precisely to make users’ lives easier.
An alternative is Electrum, available in mobile and desktop formats.
The former is a version that is not without its imperfections, and it is recommended to turn to Blue Wallet.
In contrast, the desktop variant is well developed. However, Lightning was created specifically for everyday micropayments; therefore, it would be somewhat limited to exploit it only from a computer.
There are also mobile wallets native to the network such as Breez, Eclair, and Phoenix. The former is still in the testing phase, so not suitable for ordinary users.
The other two, however, are downloadable and immediately available. Be careful, however: while Blue Wallet is widely used, these variants are far from famous and proven. Therefore, handle with care.
"Blue wallet is really well developed. Unless you have specific needs, this is probably the best choice for interacting with the network"
Lightning Network: efficiency in the service of Bitcoin
Bitcoin has as much potential as its limitations.
Strengths continually collide with weaknesses that limit its use cases. In fact, without layer 2 support, bitcoin is a fantastic coin for preserving value but inefficient for the vast world of micropayments.
Over time, alternatives have sprung up to take its place in this regard: think Solana, just to name one.
However, Lightning Network is here precisely to fix things and make BTC a perfect payment medium as well.
We are in the presence of a very cleverly thought-out technology with very high scalability. Sure, some limitations are there but they can always be remedied.
While well known, Layer 2 Lightning has the misfortune of not being as well known as the alternatives that have arrived over the years. In fact, there are people with a fair amount of background in cryptocurrency who either do not know about this network or have only heard its name.
This is really a pity: Lightning lacks nothing at all and could already serve a decidedly large user base, worldwide, at almost no cost and safely.
The positive news lies in the continued growth over time. Therefore, it is likely that adoption will continue and more and more people will find in Lightning Network what they have been looking for. Let’s wish it well because this Layer 2 is not only a great service: the greater its use, the greater the intrinsic value gained from its Layer 1 Bitcoin!
Were you already aware of Lightning Network? Have you tried using it? If you wish, our socials are there waiting for your input.

