Avalanche, the “platform of platforms”
Avalanche (AVAX) is an open source platform for decentralized application development.
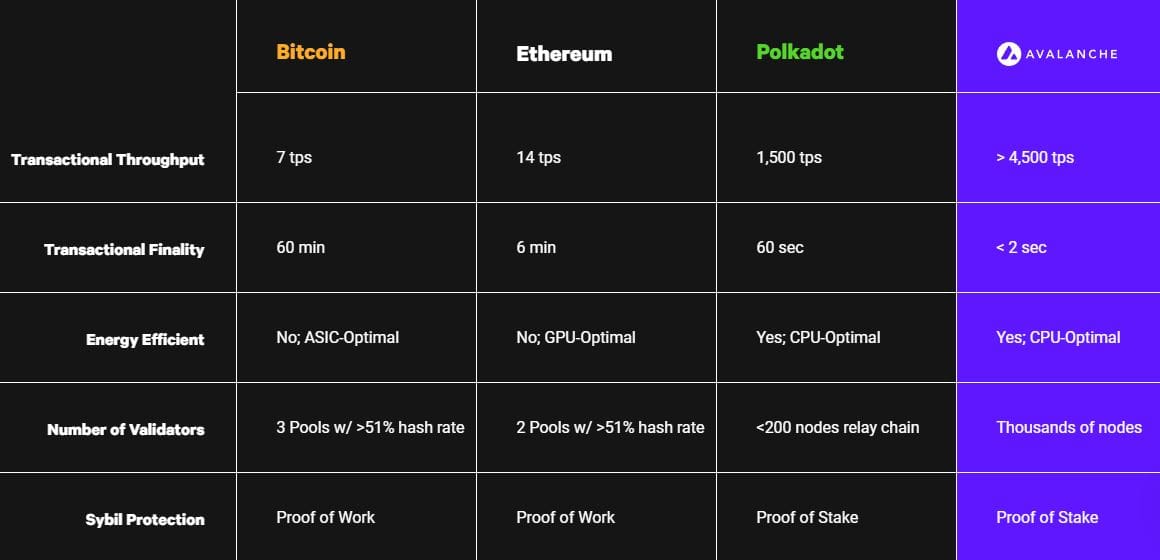
Blockchain support provides an interoperable and highly scalable system. Using the Proof-of-Stake consensus algorithm, it allows thousands of validators to have a say in maintaining and updating the network while consuming as little energy as possible.
The Avalanche network aims to create a plug-and-play system that allows different platforms to take advantage of the innovative consensus system, scalability and ease of asset creation. It is a platform for platforms to enable a series of “sub-networks” (subnets) to create a unified marketplace.
Avalanche develops its own consensus protocol aimed at writing an orderly and linear blockchain, this system is called the Snowman Consensus Protocol.
Index
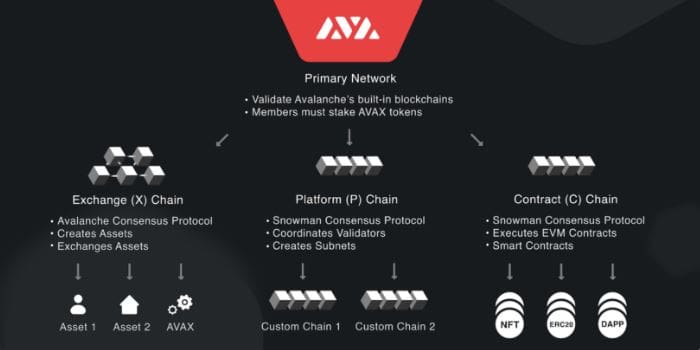
Primary Network and blockchain integrated
In Avalanche, each validator of the subnets must also be validator of the Primary Network by staking at least 2000 AVAX, the project’s native cryptocurrency. In addition:
- A subnet or subnetwork is a dynamic set of validators working together to reach consensus on the status of a set of blockchains;
- Each blockchain is validated by a single subnet;
- One subnet can validate multiple blockchains;
- One node can be part of several subnets.
The Primary Network contains three blockchains within it:
- Platform Chain (P-Chain): the P-Chain is Avalanche’s infrastructure; it coordinates validators, keeps track of active subnets, and enables the creation of new ones. Thanks to the P-chain, the Snowman validation protocol is implemented. By connecting to the P-chain API, users can create new subnets, add validators to existing ones, and create new blockchains.
- Contract Chain (C-Chain): the C-Chain enables the creation of smart contracts on the network through its API’s. The C-Chain is a version of the Ethereum Virtual Machine promoted by Avalanche.
- Exchange Chain (X-Chain): the X-Chain acts as a decentralized platform that enables the creation and trading of digital assets. These are representations of real-world assets (e.g., equity, bonds) characterized by rules governing their nature, such as “restricted to US citizens only,” “not tradable until day x,” and so on. One of the assets on the X-chain is AVAX; in fact, whenever you want to execute a transaction in a blockchain on Avalanche, you pay fees in AVAX. The X-Chain is part of theAvalanche Virtual Machine (AVM). The X-Chain API allows users to create and trade assets on the X-chain.
"Each subnet validator must be a Primary Network validator by staking at least 2000 AVAX"
Avalanche-compatible wallets
Decentralized finance fully empowers its users. The security of our funds depends on how thoughtful we are in making transactions with our addresses and how secure we keep wallet accesses.
Think of an address as a safe and the wallet as a key to all safes. The wallet is accessed by providing the private key, which is unique and consists of 12/24 words.
Losing private keys means you permanently lose access to your wallet; as of today, there is no way to recover your assets!
At the same time, anyone who comes into possession of your private key can access your funds and withdraw all your assets. Therefore, it is vital to make sure that no one else comes into contact with your passphrase. It is a useful practice to never store your keys on an online device.
In order to access the Avalanche network we can use the platform’s native wallet, Avalanche Wallet, or, thanks to the development of C-Chain it is possible to interface to the various dApps, thanks to MetaMask.
You should access your wallet through the use of a hardware wallet; if you don’t have one yet to keep your private keys secure, I recommend you give this article on Ledger Nano X or the one on Trezor a read.
To move your funds from X-chain to C-chain you can use Avalanche Wallet.
To test and verify the functionality of the C-chain, we can ususf the testnet, thanks to which we can operate on the various dApps with virtual funds, allowing us to test various strategies at no cost.
To send funds to our wallet we will need a Test Network Faucet (https://faucet.avax-test.network) where we are going to paste our testnet address to which our tokens will be, after the simple passage of Chapta and “Request AVAX,” sent.

Proof-of-Stake Avalanche
Staking is that process by which we block tokens, in order to support a network from a security perspective, we are rewarded proportionally to our contribution. The concept of staking was introduced primarily by Sunny King and Scott Nadal of Peercoin.
To resist a sybil attacks (51%), a decentralized network provides that the weight of the individual’s influence is based on the distribution of a scarce asset.
This should prevent an “attacker” from gaining enough influence over the network to compromise its security, since the cost of the operation would exceed the gain.
In a PoW system the scarce commodity is computing power, in Avalanche’s proof of stake it is the native AVAX token.
In order to validate blockchain on Avalanche, a node must necessarily staking the AVAX coin.
"A decentralized network predicts that the individual's weight of influence is based on the distribution of a scarce asset; in Avalanche's PoS it is the native AVAX token."
Validators and Delegators
Validators secure the Avalanche network by creating new blocks and processing transactions. The probability of one node being chosen over another is a function of the stake weight.
When you add a node to the set of validators you specify the following information:
- Your node ID;
- When you want to start/end validation;
- How many AVAXs you wish to put in staking;
- The address to which any rewards should be sent;
- The interest rate you want to apply to delegations (min 2%).
Delegators are token holders who want to participate in staking by deciding to rely on an existing validator, via delegation
When you delegate staking to a validator you specify the following information:
- The ID of the node you are delegating to;
- When you want to start/end your delegation period (must be concurrent with the node’s validation period);
- How many AVAXs you are delegating;
- The address to which any rewards should be sent.
If the validator to whom you are delegating your tokens is sufficiently active in the validation period you will receive the rewards when the delegation expires. Delegators are rewarded according to the same process as validators except for the predetermined percentage that the validator retains (delegation fee).
When you start the delegation process, the delegated tokens and delegation fees are deducted from the wallet you control while at the end of the delegation period, the delegated tokens return to your address and any rewards will be credited to the specified address.

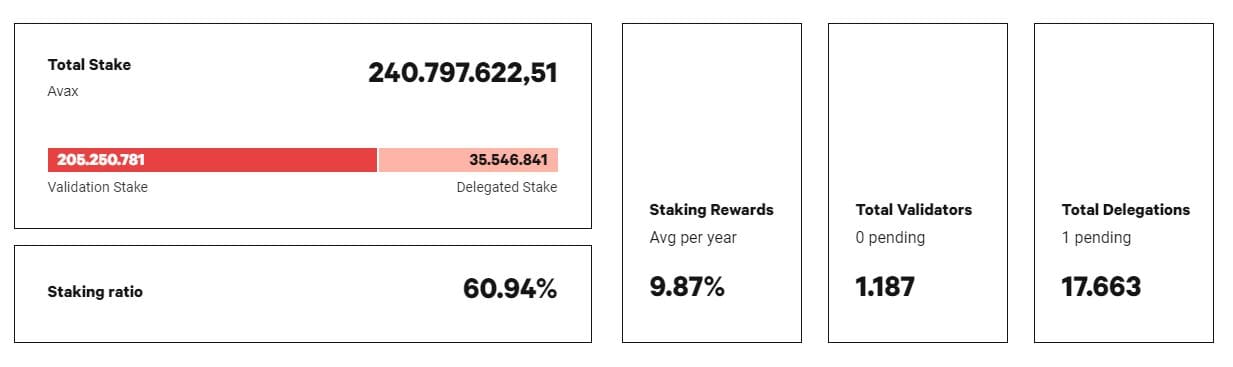
AVAX staking parameters.
Those who stake their AVAXs by posing as validators can have them back only when the staking period ends and can receive rewards, based on their participation in making the network secure.
A validator receives rewards only if his node is active and working properly for 80% of the validation period, this is done to mediate on the large number of validators, the node should be active and working properly 100% of the validation time.
To better understand the staking mechanisms of AVAX network, a comprehensive and dedicated whitepaper is available in the official AvaLabs documentation
In addition, the following parameters must be met in order to receive rewards:
- The minimum amount of AVAX that a validator must put into staking is 2000 AVAX;
- The minimum amount of AVAX that a delegator must delegate is 25 AVAX;
- The minimum time period required for validation is 2 weeks;
- The maximum time period for validation is 1 year;
- The minimum time period required for delegation is 2 weeks;
- The maximum time period for delegation is 1 year;
- The minimum interest rate for delegation is 2%.
Ecosystem of Avalanche
Avalanche is a smart contract platform for decentralized applications, but what can we actually do on Avalanche? Let’s look together at the pillars on which the ecosystem rests:
- Decentralized exchange: you can exchange your assets through different DEXs developed on the network (Trader Joe, SushiSwap)
- Yield Optimizer: (Yield Yak, Beefy Finance)
- Borrow Lend (BENQI, Aave, Curve)
- Buy NFT (Curate, Flashback)
- Manage your portfolio (Markr, DeBank, Ape Board)
Major multichain platforms, such as Aave, Curve, and SushiSwap, were immediately open to working with Avalanche.
Platforms that need high requirements for scalability and instant finalization choose Avalanche (AVAX) for the development of their dApps but not only that, many platforms to date, are “community-driven” and Avalanche offers a rapidly expanding ecosystem focused on delivering a great DeFi experience to its users.

How much is an AVAX worth?
The price of AVAX can be monitored on all platforms dedicated to cryptocurrencies, such as CoinMarketCap and CoinGecko.
For the discerning, however, we recommend TradingView, the platform of choice for technical and fundamental analysis on Avalanche price action. Here is the AVAX/USD chart:
Is Avalanche a good crypto?
Can AVAX be worth investing in? And how risky is AVAX?
The starting point is the value of the network: Avalanche AVAX is a stable, established and continuously developing entity, so we are not dealing with exotic or dubious projects.
But is AVAX better than Ethereum? This probably only time will be able to clarify, but it is undoubtedly a coin to consider if you want to diversify among various smart contract platforms.
Otherwise, the answers depend from person to person. Those with a low risk tolerance might not like this coin; those with a higher threshold might find AVAX an excellent opportunity.
We therefore leave it up to each investor to decide for themselves.
Conclusions
We conclude this focus on the Avalanche blockchain by summarizing what are its main features:
- Avalanche is a blockchain PoS, which allows the integration of different applications and blockchains, Plug-And-Play Network
- The Primary Network, the coordinating blockchain, thanks to the innovative consensus system allows the almost instantaneous finalization of numerous transactions.
- We have three networks, P-Chain (Consensus Platform), C-Chain (EVM contracts), X-Chain (AVAX, Avalanche Virtual Machine)
- Defi ecosystem that is expanding rapidly, thanks to EVM compatibility and network features: scalability, instant finalization, and low cost.
In short, Avalanche would seem to have all the makings of a major innovation center for the future of decentralized finance.
But not only that, from the characteristics of the network, it is immediately clear that Avalanche also wants to be a support for companies that, thanks to their blockchain have gained advantages, but need a main infrastructure to which they can delegate security and efficiency in transactions.

