What is Polkadot used for?
Polkadot was created to address a scalability and interoperability problem. It is an infrastructure where different blockchains can be developed, allowing each to operate efficiently and separately.
The development of Polkadot is authored by the Web3.0 Foundation. This entity was created by Gavin Wood, one of the minds behind Ethereum.
Among the Foundation’s various activities, important is the support and development of decentralized web protocols, paying attention to the use of innovative cryptographic systems.
To do this, Pokadot employs a sharding mechanism. In short: blockchains are split into several sections so as to ease the work of individual validators. These can focus on validating only the section designated to them, improving performance. Coordination of the various shards, called Parachains, is designated to a central network.
Through this construction, Polkadot is able to provide a substrate for projects seeking scalability and independence. A true base of operations where one can find all the tools to develop one’s idea.
There’s more: by allowing the sharing of all kinds of data between projects, here is opening up a potentially infinite number of use cases. Polkadot aims to provide a starting point for the development of new markets and opportunities.
Index
Web 1.0, Web 2.0, Web 3.0
In the early 2000s, when the Internet was becoming the focus of many people’s attention, few were its use cases. Usage was static and constrained to reading web pages only.
The virtual world was taking its first steps into the future, creating the first read-only data line on the network and some tentative digital identities. This stage of Internet development is also called Web 1.0.
With the growth of online businesses and social platforms, the Internet needed to evolve to version 2.0.
This upgrade, current version of the Internet, allows dynamic and interactive use of web pages. Users can read and write information on the net, deciding whether to make uploaded information public or private.
Despite the improvement, this guise of the Internet still faces problems related to security and privacy. Among them, the progressive centralization of user data creates inconveniences from a trust perspective. Here, then, is where the new version comes in.
Web 3.0 enables a shift from centralized network management to a decentralized system, where it is the user who is in control of his or her own data, without the need to trust third parties. The goal of Web 3.0 is precisely to create an infrastructure without intermediaries in which people can regain control of their digital identity.

Polkadot: blockchain interoperability and scalability
Now that we know what Polkadot is, let’s go deeper into how it works.
Polkadot provides the tools to overcome the limitations holding back the adoption of blockchain technology: scalability and interoperability.
The emergence of bridges and the adoption of EVM (Ethereum Virtual Machine) have so far worked as a palliative to allow the crypto industry to evolve by creating synergies between different projects. However, there remain underlying problems related to the scalability of Ethereum and the security of bridges.
Creating the foundation on which a decentralized web can be built: this is the mission of Polkadot, a layer-0 of creation and coordination that gives projects full control over the development of their own applications. To learn more about the layer concept, here is the in-depth look at layer-0, layer-1 and layer-2.
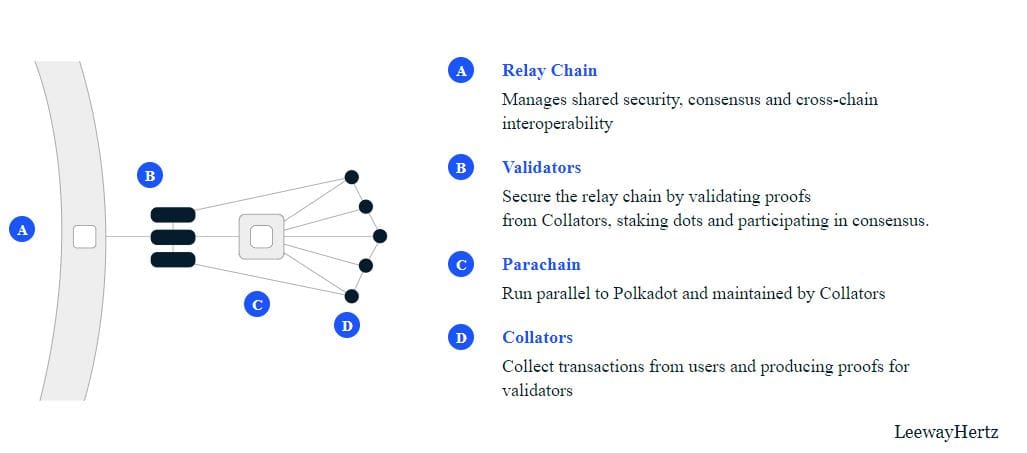
Polkadot brings together a heterogeneous group of shards called Parachains. These networks are connected and coordinated by the Polkadot Relay Chain, as well as being set up to connect to external realities via communication bridges.
Let’s move on to the key roles!
Roles in the Polkadot network
Let us now look at the key roles that can be filled within the Polkadot DOT network. These mainly help to keep the state up-to-date and secure.
In Nominated Proof of Stake blockchains, the roles are as follows:
- Validators: those who actually finalize the blocks in the network (polkadot staking), receiving the information generated by the various parachains and making it compatible with the Relay Chain. Staking of the DOT coin will be required to enable securing the Relay Chain, receiving a reward proportional to their contribution.
- Nominators: nominators are those who help secure the network by selecting a number of validators they trust and staking their Polkadot DOTs with them.
- Collectors: full nodes of the polkadot parachains, they process user transactions and send them to validators so they can be verified and added to the Relay Chain. They delegate the finalization of transactions to the Validators.
- Fishermen: as we have also seen for the Elrond blockchain, this role allows them to monitor the network and report any malicious behavior to the validators.
Let’s take a look at governance, which is particularly important for projects of this type.

Polkadot Governance
The goal of Polkadot’s Governance system is to ensure that the majority of the network has the reins and influence to direct the network.
To do this, active stakeholders in the ecosystem are asked to choose a council of onchain entities to represent the majority and to streamline decision-making processes. Although it currently consists of 13 members, each decision must be approved by referendum; each user, in proportion to the weight of participation, expresses his or her preference on the matter.
The council members, elected to represent stakeholders, have mainly two functions:
- Propose referendums, i.e., votes on changes related to the network;
- To veto those votes with malicious or dangerous purposes.
The Technical Committee is composed of the active members of the development team. It can propose emergency referenda by cooperating with the Council in order to speed up the voting and implementation process.
DOT: Polkadot's native coin.
DOT is the native coin of the Polkadot network. It can be used in governance processes, to pay network gas fees, to obtain staking rewards, to participate in parachain auctions, and many other features.
Depending on the amount of coins owned, one has access to different services:
- 1 DOT: minimum required to have an active account on Polkadot. In fact, accounts that have a lower balance cannot perform transactions. Always make sure you have some tokens in the polkadot wallet; in case the total amount of DOT held falls below the minimum value, the account will be disabled so as not to burden the network. You will still be able to access it and the funds are safe; however, you will need to make a rehabilitative deposit that will bring the balance back above the threshold.
- 5 DOT: Minimum contribution required to start a consensus collection during Parachain auctions. Through these events, projects will be able to obtain the parachain slot and develop in the Polkadot substrate.
- 20 DOT: Amount required to register one’s onchain identity, as well as to participate in voting for council members. Up to 16 members may be chosen for election and voting will be equally divided among them.
According to Polkastats data, there are currently approximately 400 active validators and more than 20,000 nominators, with a total of 617 million coin DOT in staking.
How many Polkadot crypto exist? According to CoinMarketCap’s verified data, the supply in circulation is approximately 1.25 billion Polkadot DOTs. In the past year, the coin has often found itself fighting for a place among the major cryptocurrencies. The maximum supply has no limit.
What is Polkadot worth today? Here is TradingView ‘s chart that tracks its value in real time:
Sharding & Parachains
The Polkadot network operates according to a fragmentation of the blockchain called sharding.
Each parachain is responsible for providing the proof blocks to the Relay Chain validators. They analyze the data according to a rigorous process, after which they can add it to the final Polkadot chain. This is because it is the validator nodes in the Relay Chain that are responsible for ensuring the security of the blocks; the Collectors, full nodes of the parachains, have no responsibilities from the security point of view and do not even require special staking requirements.
We have seen that as long as a chain wants to build its infrastructure in the Polkadot substrate, the process of finalizing transactions and securing the system is delegated to the Relay Chain.
But what happens when you want to do a transaction with a chain that uses its own finalization process, such as Bitcoin?
Polkadot develops an interoperability technology called Cross-Consensus Message, which can make both incoming and outgoing transactions compatible. Not bad!
Where to buy Polkadot?
Where to buy Polkadot DOT? Good news: this is a cryptocurrency available on all major crypto exchanges. Here are a couple of names (and their referrals) to help you choose:
- Binance: the industry giant offers several exchange pairs with DOT. The Binance referral entitles you to 20% off fees forever;
- Bitget: exchange with lots of liquidity and high volumes. My Bitget referral brings a 15% fee reduction forever;
- Coinbase: very famous platform also listed on Nasdaq; higher fees but maximum ease of use and security. Here’s the referral.
Prefer a DEX, i.e., decentralized exchange? No problem: PancakeSwap is at your service!
What about polkadot predictions? What might the future hold?
The year 2022 brought significant losses to the entire crypto sector (and beyond). Polkadot DOT has not been outdone and the ATH (all-time high) above $50 is a distant memory. Now the ecosystem is consolidating and renewing itself for the future.
How much will Polkadot be worth? Question we cannot answer. Since we cannot predict what lies ahead, we must “limit ourselves” to reasoning about the fundamentals. The quotation mark is in order: if a project is good, the odds are significantly higher that it will perform well again.
Polkadot is a technically advanced and innovative infrastructure that so many developers invest their efforts in every day. Should blockchain and cryptocurrencies come back stronger than before (which we believe in), it is highly likely that this reality will go to fill a prominent role.
In any case, do your own research before investing: never blindly trust the judgment of others and do not take the Polkadot predictions out there at face value.
Final thoughts on Polkadot
Polkadot focuses its attention on solving scalability and interoperability problems. Not surprisingly, it is funded and directly supported by Gavin Wood’s foundation: he may have lived with these problems in the phase of work devoted to Ethereum.
When one understands the nature of the problem, it is easier to study a solution. In fact, one understands the dynamics that cause the problem and focuses on how to prevent them.
Polkadot has all the makings of being one of those project-calamites of innovations and big ideas.
Parachain auctions started in late 2021 and are proceeding steadily. There is already the ability to communicate with other EVM platforms, so it will be time and ability to evolve that will sanction the ultimate entry to the big boys’ table. Use cases are increasing and bode well.
Fully understanding the dynamics of how this works is not so simple or straightforward. Then again, each technology involves more technical and in-depth aspects that are only within the reach of insiders. We hope we have given you a clear overview of the features that distinguish Polkadot.
What do you think of this project? Do you think the future is interoperable or will tribalism prevail?

