Polygon: the sidechain of Ethereum
Polygon is the highly regarded network that breaks down the limitations of the Ethereum blockchain through various technical solutions.
In this in-depth study we will study Polygon and answer several questions, including:
- What is Polygon MATIC?
- What is Polygon MATIC used for?
- What are the benefits that come from this sidechain?
Since its inception, Ethereum has received increasing interest, largely due to the innovative ideas behind the project. Just think of smart contracts, the building blocks of the DeFi world, which originated on this very blockchain.
Or, how can we forget the Non-Fungible Tokens, assets that have given birth to digital art and reference platforms such as OpenSea.
Let us begin to study Polygon by starting from its very base.
Index
- Polygon MATIC: solution to the limits of its layer 1
- What is Polygon MATIC?
- Is Polygon competing with Ethereum?
- What is coin MATIC?
- How much is a Polygon worth?
- Where to buy Polygon MATIC?
- Operating on Polygon: Metamask configuration and exchange
- Polygon's DeFi: a comprehensive and compelling offering
- Polygon: beyond the limits
Polygon MATIC: solution to the limits of its layer 1
Its enormous success has placed Ethereum in the Olympus of the blockchain and crypto industry, becoming the inspiration (and model to copy!) for so many others that have come along over the years.
The numbers of the chain devised by Saindeep Nailwal are growing, but there is a huge barrier to overcome: the limits of the creature itself.
Ethereum’s first problem lies in its scalability.
Until September 2022, the chain operated according to the Proof-of-Work consensus algorithm, already mentioned in so many of our insights.
This process, better known as mining, is safe but very energy- and computationally-intensive. This made the maximum number of transactions per second decidedly limited (about 30), with all the disadvantages that this entailed.
Due to high demand, long waits were created; in addition, also complicit with the “auction mechanism” regarding gas fees, transaction costs were very high. Anyone who had even moved ETHs from one wallet to another in 2021 knows what we are talking about: absolutely insane figures.
The transition to the Proof-of-Stake consensus algorithm that took place through the September 2022 Merge was a hugely important event, underpinning the famous blockchain’s transition to scalability. However, many steps remain to be taken, and no matter what, Polygon will still have a place among the networks.
The second problem concerns the limitation to the ERC-20 world.
Sure, tokenization can be used (making ERC-20 what it is not) but it is not a clean solution to the problem, it is more of a workaround.
Polygon was born a few years ago, when updates on layer 1 had not even been thought of. Polygon’s goal is to overcome the limitations of of of the parent blockchain, making life easier for users, investors and developers.
Many people claim that Polygon is an antagonist of his Layer 1: well, nothing could be more wrong, we will see in the next paragraphs.
In addition, some refer to this network as a sidechain. Others call it layer 2. Let’s say no one is wrong but it is something more. For convenience, we will refer to it as a sidechain, but explain the nature behind it.
Well, now we can start working in earnest. Let’s start with the basics and find out what Polygon is.
What is Polygon MATIC?
Polygon is a sidechain of Ethereum. Confusion? No problem, we immediately clarify the meaning of this terminology.
Layer 0, layer 1 and layer 2 represent different levels of the blockchain world. Each of them has specific purposes and can be optional (layers 0 and 2) or indispensable (layer 1).
Layer 2s are designed to offer something extra and improve the chain on which they rest. Polygon has exactly this mission: to give added value to its Layer 1.
Polygon crypto, however, is a sidechain. Unlike the average layer 2, which is totally subordinate to the parent chain, these networks have some independence.
In the case of Polygon there is in fact its own Proof-of-Stake algorithm, a dedicated validator network, and a native coin (MATIC) equipped with various purposes that we will discover below.
Therefore, this layer 2 moves with more freedom than many other known ones such as Arbitrum.
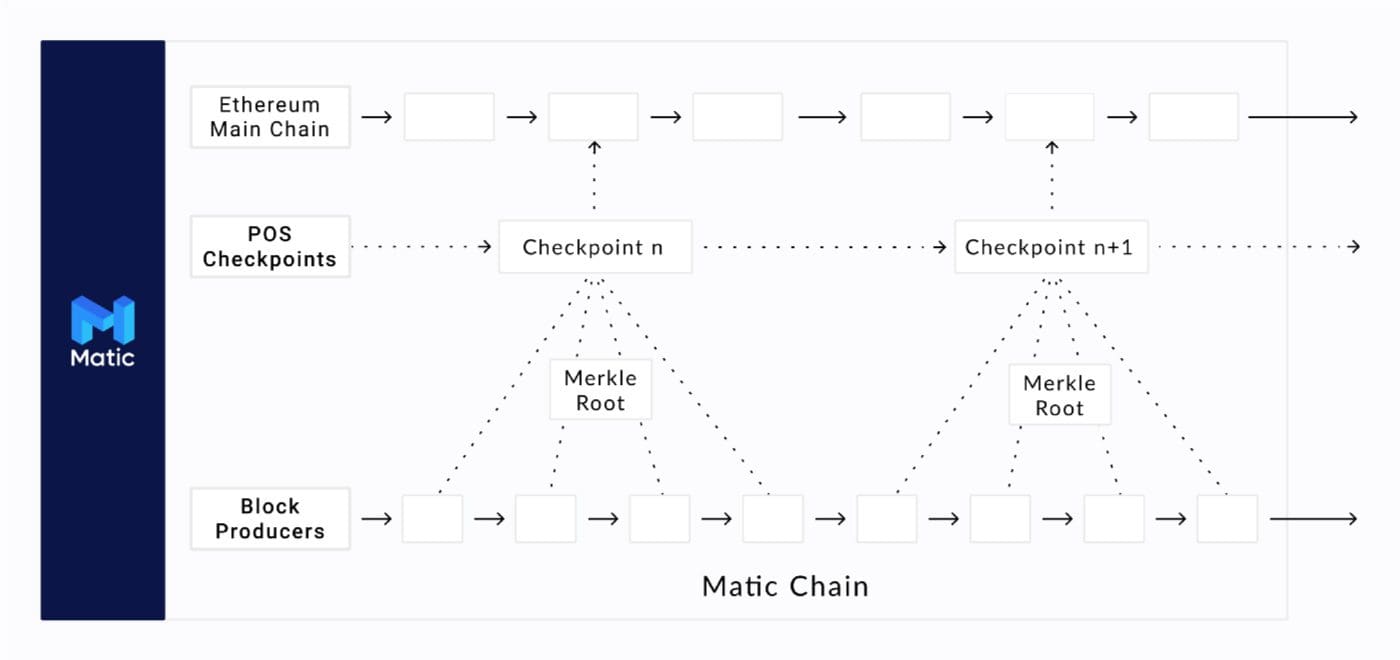
The image above, taken from the official documentation, illustrates how Polygon works; it especially highlights the key steps where there is interaction with chain layer 1.
Note: the photo shows the inscription Matic Chain, which is the name by which the network was originally christened. Therefore, when you encounter images or documents bearing Matic, there is no mistake: you are still talking about Polygon.
As we can see, Polygon moves parallel and independent. This is because there is a consensus algorithm and validators dedicated entirely to the network, without having to rely on the help of the parent chain.
From time to time, however, there are checkpoints: this is where Polygon comes into contact with blockchain layer 1. In fact, the latter acts as a controller and ensures that layer 2 acts without error, preventing manipulation and accidents.
So what is one of the advantages of Polygon over Ethereum? In truth, proceeding by this mechanism, there are many advantages.
First, we just said it, Polygon becomes a safe and stable environment.
On the other hand, layer 1 does only a fraction of the work it would have to accomplish if Polygon Matic did not exist. Therefore, the chain benefits in terms of congestion.
But not only that. More specifically, Polygon has these two strengths:
- High scalability: Polygon can process tens of thousands of transactions per second, all at a negligible cost. In fact, all operations involving smart contracts are passed from the parent chain to Polygon (an operation called rollup).
- Interoperability: layer 1 is already multi-chain but not able to deal with the huge amount of work involved.
Polygon makes it possible to build ad hoc solutions for a variety of needs, up to and including new layer 2 and even standalone blockchains (totally independent with their own consensus and validators).
This is all possible thanks to the Polygon SDK, a set of tools created for programmers that can make the development of the above agile.
Polygon is the tool that breaks down the problems of its layer 1, as well as a rival to other well-known entities such as Polkadot and Cosmos (although each has its own peculiarities).
The situation is a little clearer. A question may arise, however: “Doesn’t Polygon compete with Ethereum?”
Let’s find out the answer in the next section.
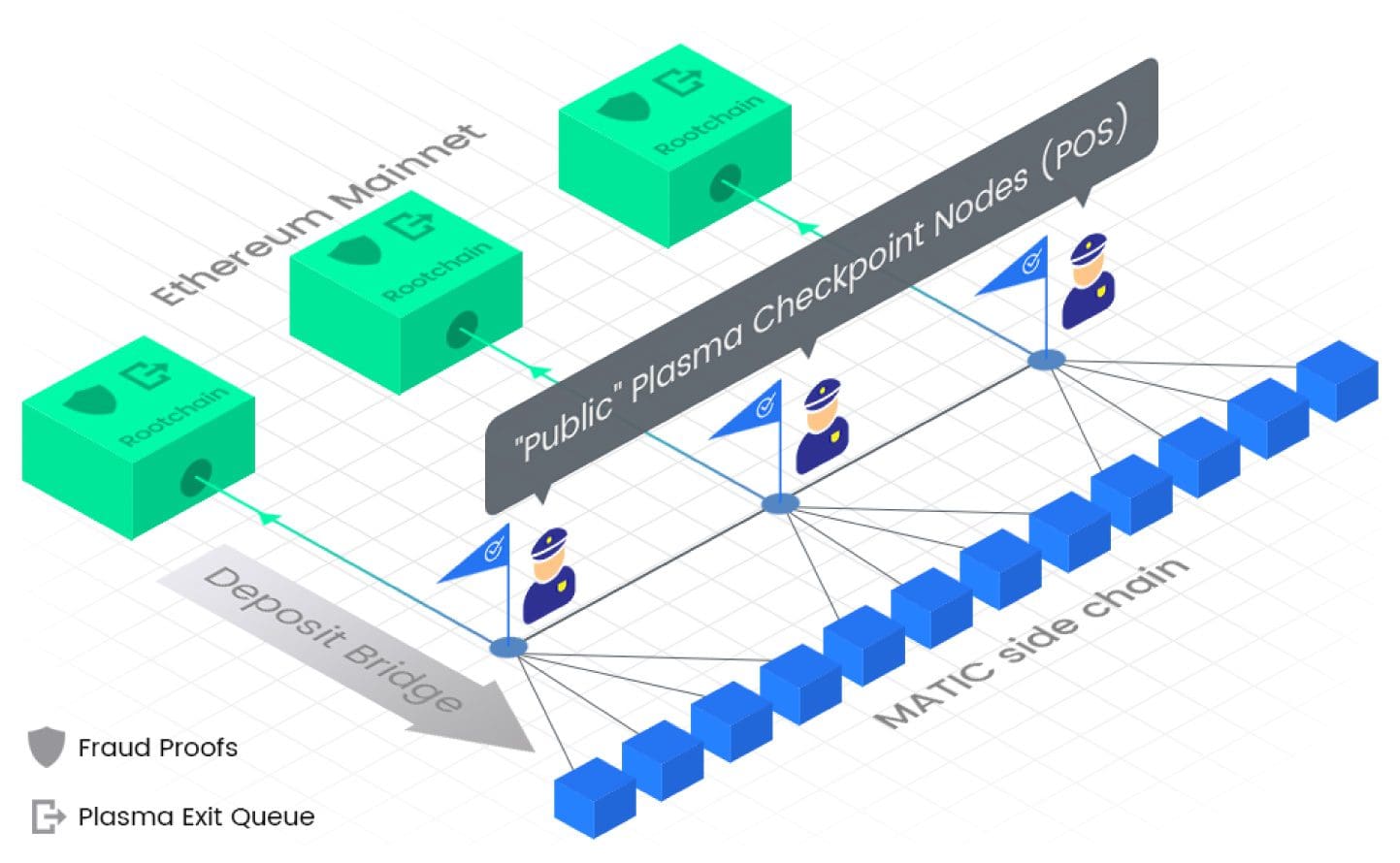
Is Polygon competing with Ethereum?
On Polygon you really hear all kinds of things.
A totally wrong but frequent claim is the one that paints this chain as a competitor to Ethereum.
Polygon has a certain independence, this is true. However, its foundation still rests on layer 1; without it it could not function.
We have repeatedly pointed out the technical limitations of its main blockchain: Ethereum is a secure and proven network but rather slow and expensive.
Also, related to the above, there is the problem of interoperability, especially on two aspects:
- It supports only ERC-20 tokens.
- It would not be able to handle the enormous traffic resulting from connecting with multiple ecosystems.
Polygon does not replace or steal users from the parent chain; rather, it expands its offerings.
First of all, speed and cost: fast transactions and insignificant gas fees.
Then interoperability: in addition to DApp deployment, Polygon makes it possible to create sub-networks, layer 2 and standalone blockchain. All compatible with EVM and bridge between Ethereum and chains developed with Polygon SDK.
The parent blockchain is thus positioned at the center of the whole system and holds the role of co-player.
When making assessments on a project, one must consider everything in front of us.
In this case there is a network, Polygon, with some intrinsic value that is likely to increase over time. MATIC, its coin, will follow the eventual positive trend.
Polygon, however, is part of a larger ecosystem and should also be included in the latter’s fundamental analysis. If the former did not exist, investors might opt for other solutions outside this macro-ecosystem.
It matters little if the gas is not paid in ETH-it is still a network that increases the value of Ethereum, enhances it, and greatly expands its proposition.
"No rivalry: Polygon expands Layer 1 ecosystem, propelling it to new horizons"
What is coin MATIC?
MATIC is Polygon‘s coin, responsible for some important tasks.
First, it is the currency in which transaction gas fees are paid. As we said, Polygon is a sidechain that does not employ ETH for this task.
This makes MATIC an attractive asset: the more the DeFi and Polygon ecosystem is utilized, the greater the demand for this gas payment coin.
MATIC is also the asset used to ensure security and operability of the network itself, as Polygon employs its own PoS algorithm.
Thus, there is a network of validators who are responsible for verifying and approving each of the many transactions.
Currently, the number is limited to 100, so there is no minimum limit of MATICs that must be possessed to exercise this role.
In the future, possible decentralization would likely go to introduce a certain amount of Polygon MATIC coins to be held for each validator.
Easier alternative to implement is to delegate one’s MATICs at one of these validators, getting a respectable annual interest in return.
Therefore, MATIC plays a key role in keeping the chain healthy and fully functional.
Finally, governance.
In proportion to the MATICs held, holders participate in the decision-making process of the Polygon world by voting or making proposals of various kinds.
What has been said so far assigns good intrinsic value and real use cases to this coin.
Polygon MATIC has a maximum supply of 10 billion, of which just about 90 percent is already in circulation.
On January 18, 2022, the EIP-1559 update, codenamed London hardfork, which had landed earlier on chain layer 1, was introduced.
This update is very important because it provides a gas fee burn mechanism that makes the system deflationary. By doing so, it is estimated that about 0.27 percent per year of total $MATIC supply will be eliminated.
Therefore, by adding up upgrade and supply cap, MATIC has all the makings of becoming increasingly scarce over time. As we know, with equal (or greater) demand and decreasing supply, the price increases.
Please note: what has just been said is not meant to be financial advice. We will never tire of repeating that every investor must do his or her own research before proceeding.
The fact remains that MATIC could maintain a growth path that has been in place for some time, especially looking at the trend in its entirety.
Beware, however: on September 4, 2024, MATIC will give way to the new coin POL. This event is part of the ongoing journey of change in the Polygon landscape, which aims to grow the network even more and prepare it for the challenges of the future.
What can I say, if there is interest in Polygon, this cryptocurrency can continue toward excellent goals.
"MATIC is Polygon's native coin"
How much is a Polygon worth?
Short paragraph devoted to the price of MATIC, because some may ask , “Okay, but how much does a Polygon cost?”
Note: Let us remember that Polygon is the blockchain, while MATIC is the related coin. Names are often used interchangeably, but let’s avoid confusion.
At the time of writing, the coin’s All-time High is above $2.7 per specimen, a value reached at the end of December 2021.
To monitor real-time trends, here is MATIC’s chart on the dollar offered by TradingView, the leading portal for technical analysis; sign up and take advantage of our discounts!
Where to buy Polygon MATIC?
MATIC is one of the leading cryptocurrencies on the scene, so the services that support it are numerous.
In the centralized setting, all major exchanges offer exchange pairs on MATIC. If you were without a CEX, here are some alternatives with referral links and bonuses:
- Bitget: one of the fittest exchanges, also featuring proof of reserve published periodically. Get 15% off fees and up to $8000 bonus if you sign up with our referral link;
- Bitpanda: Europe’s largest exchange, a benchmark for those who don’t want to compromise on security. Sign up for Bitpanda;
- Binance: the giant among cryptocurrency exchanges offers a plethora of services to please everyone. 20 percent off fees.
If you prefer to be in the decentralized world, Polygon MATIC is on so many DeFi platforms. QuickSwap is the largest native platform.
Operating on Polygon: Metamask configuration and exchange
Let’s move on to the operational phase and see how to enter the world of Polygon.
As a first step, it will be necessary to set up a wallet suitable for the purpose. As is often the case, MetaMask performs this task perfectly and provides the security of a noncustodial wallet.
Two versions of this popular wallet are available: the mobile app and the browser extension. Below we will see how to set up the Polygon network using the latter.
MetaMask wallet configuration for Polygon
Let’s put the record straight: nothing complex, only 2 minutes to complete.
We open MetaMask and click on the drop-down menu related to the network (see image below). We then select the Add Network button.
The parameters to be added will be as follows:
- Network Name: Polygon
- New RPC URL: one among them:
- https://polygon-rpc.com
- https://rpc-mainnet.maticvigil.com
- https://rpc-mainnet.matic.network
- https://rpc-mainnet.matic.quiknode.pro
- Chain ID: 137
- Currency Symbol: MATIC
- Block Explorer URL: https://polygonscan.com/
We save to complete the work.
Moving cryptocurrencies from Ethereum to Polygon
Now that the wallet is up and running, we are ready to switch coins and tokens from the layer 1 blockchain to Polygon.
To do this, you can use the bridge available at the previously visited site: wallet.polygon.technology/bridge. Before logging in we will be asked to connect our crypto wallet.
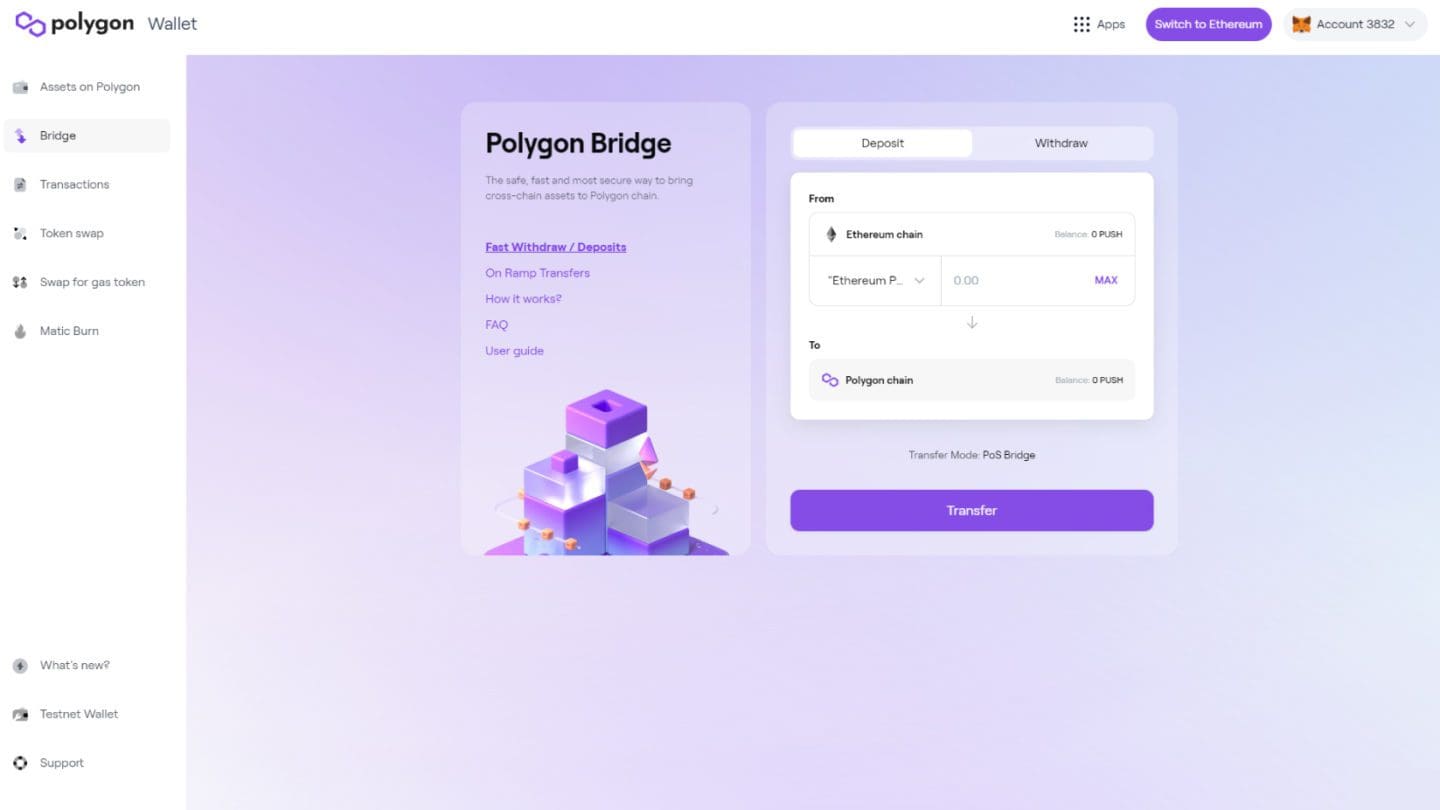
The image shows the window from which we are going to act.
Everything is very simple: selecting the Deposit or Withdraw tabs defines source and destination chains. In the example image, acting would withdraw from Ethereum and deposit on Polygon.
After that, clicking on the drop-down menu related to coin and token (pictured indicates Ether) selects the asset subject to the move.
Let’s indicate the quantity and then click the Transfer button.
Several wallet confirmations and a variable waiting time will follow. This is because Polygon Bridge will have to interact with two different chains, each with its own validators. Gas will also have to be paid according to the interactions that have taken place.
At the end of the process we should be able to view the funds in the target chain.
For those looking for an alternative method, exchanges may be the way to go; we discussed this in the previous section.
"For those who don't want to use a bridge, more and more exchanges support the Polygon network"
Polygon's DeFi: a comprehensive and compelling offering
Our analysis could not miss a part devoted to decentralized finance.
Polygon (MATIC) offers a vibrant DeFi environment that includes all major Layer 1 native protocols.
First, Curve, the most popular platform and also present on other popular chains.
This protocol needs no introduction: it is one of DeFi’s mainstays, known for its excellent construction and broad offering of investment pools and instruments.
Its only limitation lies in its old-style interface, which is not very friendly especially for less experienced users.
Nevertheless, Curve.fi is synonymous with reliability. Polygon allows you to operate there without having to worry about high costs in gas fees.
Another giant available on Polygon is AAVE, one of the largest DeFi platforms ever in terms of deposited liquidity.
The main service offered is lending. Users then have the opportunity to deposit funds and use them as collateral to borrow other cryptocurrencies, developing complex (and risky, mind you!) multilevel investment strategies. Or simply provide capital, receiving a secure passive income – not bad!
However, it would be reductive to describe AAVE only in this way because there is so much more to it. In fact, the protocol enables the exchange of cryptocurrencies and stakes the AAVE token, thereby gaining interest and participating in the platform’s decision-making process.
Polygon’s DeFi also offers native solutions designed specifically for this layer 2. This is the case with QuickSwap, the DEX that raises hundreds of millions in liquidity.
The protocol is well done and offers a wide range of tools, from simple token swaps to the Liquidity pool with farm.
QuickSwap is clearly inspired by Uniswap but not surprisingly, it is the basis for countless decentralized finance platforms.
About the latter: of course Polygon is fully supported by both it and SushiSwap, the other benchmark AMM in the crypto landscape.
The offer certainly does not end there: the famous portal DefiLlama has numerous protocols that support the Polygon chain listed. Many of these have no or very little liquidity but many others are fully operational.
Polygon thus has much to offer for investors in decentralized finance. All you need to do is get informed, choose the right solution for your needs, and get started.
Reduced gas fees allow experiments with small numbers, a great added value that guards against mistakes or unforeseen events.
One last tidbit:NFT fans will not be disappointed. The popular NFT OpenSea marketplace fully supports the Polygon chain, so you can buy or sell unique creations without having to spend a fortune on gas fees.

Polygon: beyond the limits
Once little considered, Polygon is instead a chain with high potential and value.
Why was she being “treated badly”? Probably due to the initial wrong assessment and consequent biases that remained over time.
The truth is that the basic idea is great and developments are following the right path. Thanks to the proposed technical solutions, a variety of applications can be built on this layer 2 with relative ease.
We have seen how layer 1 is at the heart of the project, arguing that Polygon exceeds its limits but does not compete with it. Indeed, the one who emerges victorious is precisely the ecosystem born from the mind of Vitalik Buterin.
In 2021 Polygon gathered increasing attention from the crypto community and continued with this trend in 2022 and 2023. Therefore, it would seem that even in 2024 this reality can continue to win acclaim and improve.

